- Why Medical Gowns Matter in Modern Healthcare
- Types of Medical Infection Control Gowns
- Medical Gown Standards & AAMI Levels
- Reusable vs Disposable Medical Gowns: Which Is Best?
- How to Choose Medical Gowns for Healthcare Facilities
- Critical Zones & Performance Testing of Gowns
- Medical Gown Compliance: Regulatory Standards
- Best Medical Gowns for Hospitals & Clinics in 2025
- FAQs on Medical Gowns
- Next Steps: Gowns in Healthcare
Why Medical Gowns Matter in Modern Healthcare

Imagine a bustling emergency room during flu season. A nurse, rushing to treat a patient, faces splashes of bodily fluids. Without reliable protection, this moment could lead to infectio-for her, the patient, or others. Medical gowns - especially surgical gowns and isolation gowns-are the unsung heroes in these scenarios, acting as a frontline barrier in infection prevention.
This guide explores everything healthcare professionals need to know about medical gowns-from types and standards to sustainability and procurement. Whether you’re a clinician, administrator, or procurement manager, you’ll find practical insights to choose the right surgical gowns healthcare settings demand, ensuring safety, compliance, and cost-efficiency.
Types of Medical Infection Control Gowns

Medical gowns are essential in reducing the transfer of microorganisms during clinical procedures, especially when designed with adjustable ties, waist ties, and thumb loops that ensure a secure fit and easy donning. A high-quality hospital patient gown should offer the highest liquid barrier protection level, with reinforced cuffs, hems, and bindings for durability. Many gowns also pair with shoe covers for full-body protection. For added safety, proper doffing techniques must be followed to prevent contamination to the wearer. All protective wear requiring premarket notification must meet strict CAD-verified design specifications and lightweight construction standards to support comfort and compliance.
Medical gowns come in various forms, each tailored to specific healthcare needs. Understanding the types of medical gowns enables facilities to select the appropriate protection for their staff and patients, striking a balance between safety, comfort, and cost.
| Gown Type | Sterile? | Fluid Resistance | Ideal Use | AAMI Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Gown | ✅ Yes | High | OR procedures | Level 3–4 |
| Isolation Gown | ❌ No | Low–Moderate | ICU/general care | Level 1–2 |
| Procedural Gown | ✅/❌ | Moderate | Dental, wound care | Level 2–3 |
Surgical Gowns vs Isolation Gowns
Surgical gowns that healthcare professionals wear are designed for sterile environments like operating rooms. These gowns, often rated at AAMI PB70 gown levels 3 or 4, provide high fluid resistance to protect during invasive procedures. For example, a surgeon performing a knee replacement relies on surgical garments to block blood and maintain a sterile field. These protective wear features reinforced fabrics and tight seams to ensure no contaminants breach the barrier.
On the other hand, isolation gown standards prioritize infection control in non-surgical settings, such as ICUs or patient isolation situations. Typically rated AAMI Level 1 or 2, this protective wear protects against infectious diseases during tasks like patient checkups or handling contagious patients. A nurse treating a patient with MRSA might wear an isolation gown to prevent pathogen spread. The key difference? Surgical gowns focus on sterility for procedures, while isolation wear emphasizes infection prevention in general care.
| Feature | Surgical Gown | Isolation Gown |
|---|---|---|
| Sterility | Yes | Often No |
| Fluid Resistance | High (Level 3–4) | Low to Moderate (Level 1–2) |
| Use Case | Operating Rooms | General Care, Isolation Wards |
Key differences:
- Surgical Gowns: Sterile, used in Operating Rooms (ORs), and offer high fluid resistance.
- Isolation Gowns: Often non-sterile, used for contact precautions.
Procedural Gowns and Non-Surgical Use Cases
Procedural gowns fill the gap between surgical and isolation wear. These clinical healthcare apparels are ideal for moderate-risk tasks, like wound care, dental procedures, radiology labs, or IV insertions. For instance, a dentist performing a root canal might wear procedural hospital wear to shield against minor fluid splashes. Protective healthcare apparel, like procedural gowns, offers flexibility, providing adequate protection without the expense of traditional surgical garments. They’re perfect for outpatient clinics or low-risk hospital departments, ensuring both safety and cost-efficiency.
| Feature | Procedural Gown | Non-Surgical Gown |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Level | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Sterility | Optional | Often Non-sterile |
| Use Case | Clinics, Dental, Labs | General Patient Care |
Key differences:
- Procedural gowns: For quick, low-risk procedures with minor fluid exposure.
- Non-surgical gowns: For general care/isolation where sterility isn’t needed but coverage is.
Medical Gown Standards & AAMI Levels
Standards like AAMI PB70 gown levels and FDA classifications guide healthcare professionals in selecting protective wear that meets safety and compliance requirements. These frameworks ensure medical gowns perform reliably in diverse scenarios.
Following medical PPE standards from the FDA and ANSI not only ensures regulatory compliance but also supports safer environments in clinics, hospitals, and outpatient settings.
What Are the AAMI PB70 Gown Levels?
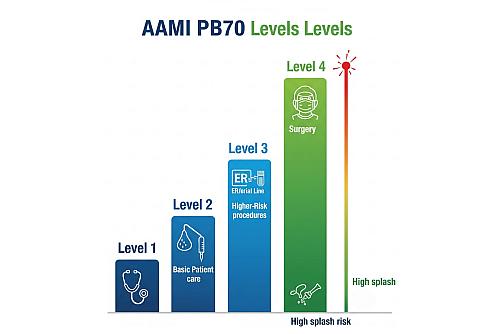
The AAMI PB70 gown levels classify healthcare apparel based on its liquid barrier protection, which is critical for infection prevention. Developed by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI), these levels range from 1 to 4:
| AAMI Level | Protection | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Minimal | Basic care, non-clinical visitors |
| Level 2 | Low | Blood draws, suturing |
| Level 3 | Moderate | ER, arterial procedures |
| Level 4 | High | Surgeries, infectious disease wards |
- Level 1: Minimal protection for low-risk tasks (e.g., basic patient care, visitors in non-clinical areas).
- Level 2: Low protection for tasks with light fluid exposure (e.g., blood draws, suturing).
- Level 3: Moderate protection for procedures with higher fluid risks (e.g., ER, arterial procedures).
- Level 4: High protection for fluid-heavy or pathogen-rich environments (e.g., surgeries, infectious disease wards).
FDA & ANSI Classification
Gowns must meet standards from organizations like:
- FDA: Regulatory classification for medical devices
- ANSI/AAMI: Standards for fluid resistance, seam strength
- ASTM Standards: Ensure hospital wear meets microbial resistance and structural integrity
The FDA classifies medical gowns as Class I (low risk) or Class II (moderate risk) medical devices, depending on their use. FDA regulatory classification requires healthcare apparel to meet ANSI AAMI PB70 classification standards for performance and labeling. For example, surgical gowns must pass stringent tests for fluid resistance and sterility. ASTM & ANSI standards ensure protective wear meets infection control gown standards, providing clear guidelines for hospital compliance. Regular audits and certifications verify that gowns align with these regulations, safeguarding patients and staff.
Reusable vs Disposable Medical Gowns: Which Is Best?

Choosing between reusable vs disposable medical gowns involves evaluating safety, cost, and environmental impact. Each option has unique advantages for healthcare facilities.
Reusable medical gowns, often made from polyester reusable gown materials, are designed for multiple uses after proper laundering. They’re durable, comfortable, and cost-effective over time. A 2023 study highlighted the benefits of reusable medical gowns vs disposable, finding that reusable gowns can cut procurement costs by 25% over five years compared to disposable polypropylene gowns. For example, a mid-sized hospital switching to reusable gowns saved $50,000 annually while maintaining safety.
Disposable gowns, however, are single-use, minimizing cross-contamination risks in high-infection settings like Ebola wards. They’re convenient but generate significant waste. The choice depends on your facility’s needs: reusable gowns for cost and sustainability, disposable for high-risk infection control.
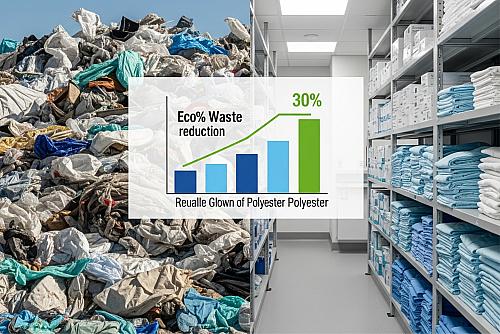
1. Environmental Impact of Medical Gowns: The environmental impact of medical gowns is a growing concern. Disposable gowns contribute to 10% of hospital waste, with U.S. healthcare facilities discarding 5 million tons annually, per EPA data. Sustainable gown materials, like reusable polyester blends, reduce landfill waste and carbon emissions. A California hospital adopting reusable gowns cut waste management costs by 30%, showcasing the benefits of eco-friendly choices. Facilities can further reduce their footprint by partnering with green-certified suppliers.
In alignment with WHO guidance, the environmental benefits of reusable gowns have been confirmed even when accounting for laundering processes—with safety and comfort maintained across repeated use cycles.

2. Laundering and Reusability Guidelines: Proper laundering and reusability guidelines ensure reusable gowns remain safe and effective. Industrial washing at 160°F with EPA-approved disinfectants kills pathogens, maintaining clean protective wear processing. Healthcare apparel should withstand 50–100 wash cycles without losing gown seam strength or barrier properties, per ASTM F3352 standards. Regular inspections for wear and tear ensure compliance with infection control gown standards, keeping staff and patients safe.
Adhering to a standardized reusable gown cleaning protocol helps facilities maintain hygiene standards while extending hospital wear lifespan.
How to Choose Medical Gowns for Healthcare Facilities

Selecting the right medical gowns requires balancing risk, protection, and budget. Here’s a step-by-step guide to make informed decisions.
a) Gown Selection Based on Exposure Risk. Protective wear selection based on exposure risk starts with assessing the procedure’s fluid and pathogen exposure. High-risk settings, like orthopedic surgeries, demand Level 4 gowns with maximum fluid resistance. Low-risk tasks, like routine checkups, may only need Level 1 gowns. A Texas hospital reduced HAIs by 15% in 2024 by aligning gown levels with specific tasks, per a case study in Infection Control Today. Matching hospital wear to risk ensures safety without overspending.
b) Barrier Protection Fabrics & Fluid Resistance Testing. Barrier protection fabrics, such as nonwoven polypropylene or reinforced polyester, determine a gown’s effectiveness. Fluid resistance testing, like hydrostatic pressure resistance, measures how well protective wear blocks liquids. Level 4 gowns, for instance, resist penetration at 20 cm H₂O pressure, ideal for fluid-heavy procedures. Fabrics should also balance protection with gown breathability and comfort to prevent staff fatigue during long shifts.
c) Procurement, Budget & Supply Chain Considerations. Procurement and cost efficiency are crucial for B2B buyers. Where to buy medical gowns for clinics? Certified suppliers offer bulk discounts and compliance guarantees.
For purchasing managers, understanding hospital wear procurement tips—such as evaluating supplier certifications and comparing volume discounts—can reduce costs without compromising safety.
Critical Zones & Performance Testing of Gowns
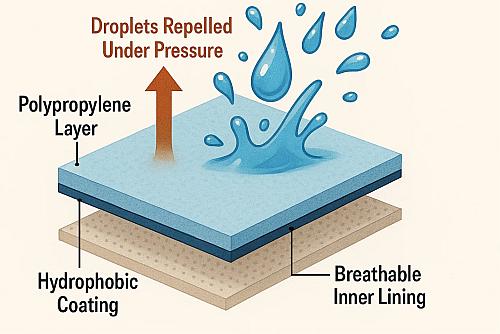
The effectiveness of medical gowns hinges on their design and rigorous testing. Understanding critical zones and performance metrics ensures optimal protection.
The critical zones of a medical gown include the chest, sleeves, and front, where fluid exposure is highest. These areas undergo fluid resistance testing to ensure no penetration occurs. For example, surgical garments have reinforced larger critical zones to block blood during operations. ASTM F1670 tests measure resistance to synthetic blood, ensuring patient wear protection in high-risk scenarios.
Gown seam strength prevents tearing under stress, tested via ASTM F2407 standards. Strong seams are vital for surgical gowns, where movement is frequent. Gown breathability and comfort reduce heat stress during long shifts. A 2023 survey by the American Nurses Association found 85% of nurses prefer gowns with high breathability ratings, improving compliance and comfort.
Medical Gown Compliance: Regulatory Standards

Compliance with regulatory standards ensures medical gowns meet safety and performance requirements, reducing risks in healthcare settings.
Infection control gown standards, like ASTM F3352, test protective wear for microbial penetration resistance. Safety compliance in clinical personal protective equipment management requires gowns to pass these tests, reducing HAIs. Hospitals adhering to these standards report 12% fewer infections, according to a 2023 study in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology. Regular training on gown use enhances compliance. Facilities that align with evolving hospital wear compliance requirements not only meet infection control targets but also reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties during audits.
The FDA regulatory classification categorizes gowns as Class I (low risk) or Class II (moderate risk). Class II gowns, like surgical garments, require premarket clearance to ensure infection prevention gown standards are met. Hospitals must verify certifications to comply with regulations, ensuring patient wear is approved for specific uses.
Best Medical Gowns for Hospitals & Clinics in 2025

Choosing the best medical gowns for hospitals in 2025 involves prioritizing safety, comfort, and cost. Here’s what to look for. When selecting clinical gowns, focus on features like reinforced seams, adjustable closures, and AAMI PB70 gown-level certifications. Top brands like Halyard and Kimberly-Clark offer the best medical gowns for hospitals with ergonomic designs and high fluid resistance. For example, Halyard’s Level 4 gowns are praised for durability and comfort, per 2024 user reviews.
Cost-efficient gowns don’t compromise safety. Reusable gowns save money in low-risk settings, while disposable gowns are ideal for high-risk areas. Protective healthcare apparel should prioritize hospital wear breathability and comfort to ensure staff wear them correctly. A 2024 study found that comfortable protective wear increased compliance by 20% among healthcare workers.
For deeper insights, explore these related topics:
- Hospital Gown Colors Meaning: Color-coded gowns streamline workflows by signaling roles or departments, improving efficiency.
- Why Patient Gowns Are Open Back: Open-back designs allow quick access for exams while prioritizing patient comfort and dignity.
- Medical Gowns vs Coveralls: Understand when to use gowns versus coveralls based on exposure risks and procedural needs.
- Hospital Linen Management: Proper linen protocols ensure patient wear hygiene, reducing infection risks through effective laundering.
FAQs on Medical Gowns

Q1. What Are Medical Gowns Used For in Hospitals?
Medical gowns protect healthcare workers and patients from infections, fluids, and the risk of contamination during procedures or routine care.
Q2. Which Medical Gown Level Do I Need?
Choose based on risk: Level 1 for basic care, Level 2 for blood draws, Level 3 for ER, and Level 4 for surgeries. Medical gown AAMI level comparison helps clarify needs.
Q3. Are Reusable Medical Gowns Safe and Compliant?
Yes, reusable medical gowns are safe if laundered per laundering and reusability guidelines, meeting infection control gown standards.
Q4. How Do Medical Gowns Meet Infection Prevention Standards?
Gowns undergo fluid resistance testing and comply with ASTM & ANSI standards to block pathogens, ensuring medical gowns comply with hospitals.
Q5. What’s the Difference Between Surgical and Isolation Gowns?
Surgical gowns healthcare professionals use are for sterile procedures, while isolation wear standards focus on infection control in non-surgical settings.
Next Steps: Gowns in Healthcare

Medical gowns are indispensable for ensuring safe healthcare environments. Understanding protective wear types, standards, and selection criteria empowers healthcare professionals to make informed procurement decisions.
Next Steps:
- Explore certified suppliers
- Contact us for a free consultation
Explore our other resources to deepen your knowledge on color codes, open-back designs, coverall comparisons, and linen protocols.

